Applications of Linear Heat Detection
Linear Heat Detection is the terminology used for fire detection systems which are used to monitor environments over a long range distance (linear assets), typically in a special hazard environment. Linear heat detection systems can detect a fire anywhere along the length of the linear heat sensing cable, and can be of lengths in excess of multiple kilometers. Fiber optic distributed temperature sensing is one of the key technologies which is utilised within this field.
There are a wide variety of industrial applications which benefit from using linear heat fire detection systems these include:
Roads and Tunnels
Due to the constrained nature and construction of road and rail tunnels,they tend to have limited escape scenarios and restricted ventilation, it is key to have an effective fire detection system for early detection to enable fire control and to prevent loss of life.
- Safety of tunnel users and owners
- To ensure continual availability of the tunnel
- To ensure trouble free operation
- Minimise maintenance work
Causes of fire include motor vehicle accidents, combustion of materials within the tunnel (including debris, oil spills) and electrical faults.
Fires and field tests have shown that the temperature of burning vehicles in tunnels rises much more quickly than can be expected in a normal fire. How quickly and in which direction smoke and gases move depends on various factors, such as:
- The extent of the fire (fire load, intensity)
- The ventilation system
- The natural air currents
- The smoke venting system
- The profile and pitch of the tunnel
One of the issues with point type fire sensors is that if the seat of the fire does not happen to be immediately under a sensor, the fire can no longer be detected with certainty, mainly due to detector spacing. Linear heat detector systems do not have any such “gaps”, since the radiation heat given off by the fire is applied over the continuous length of linear heat sensing cable, and is recorded and displayed accordingly.
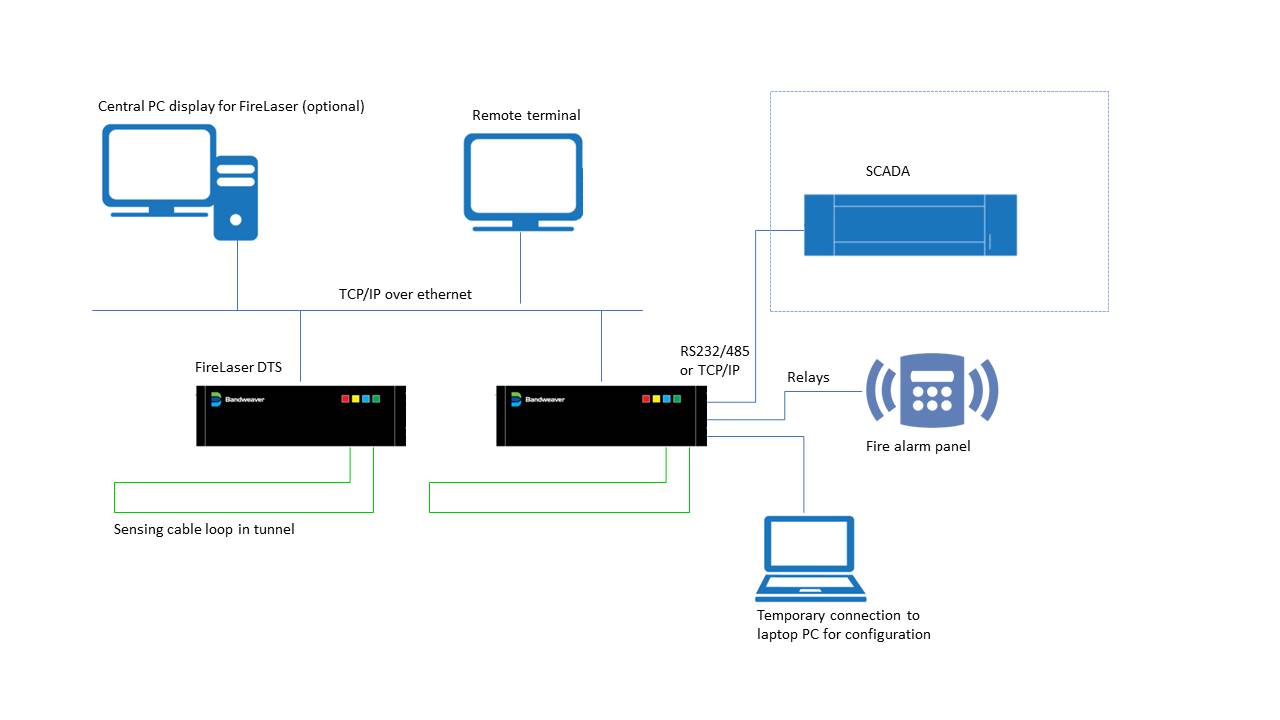
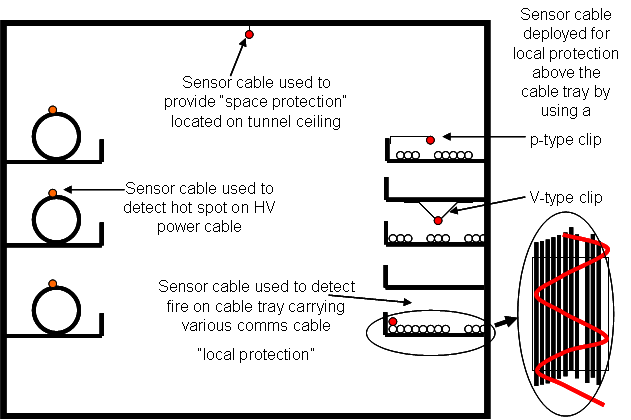
Cable Tunnels and Cable Trays
DTS technology has been extensively used to protect cable trays and cable tunnels. These are two distinct applications within this environment. Fires in cable tunnels are not frequent events but such events can have a significant financial impact on the owner companies due to the vital business related data and services that these critical “arteries” may provide. Fires in such environments, if not detected quickly, can pose a significant danger to the owner companies in terms of protection of personnel as well as the company’s assets. High intensity fires can produce significant quantities of toxic smoke and fumes which may hinder the escape of trapped personnel and the ability for fire and rescue services to gain access to extinguish the fire. It is therefore important to be able to determine the location of the origin of the fire event in an effective and efficient manner.
The main fire risks associated with cable tunnel and cable trays are due to:
- Faulty electrical cables within the cable trays
- Faulty electrical equipment used to control the tunnel environment
- Associated hot works which may routinely be carried out
- Build-up of flammable materials discarded by personnel
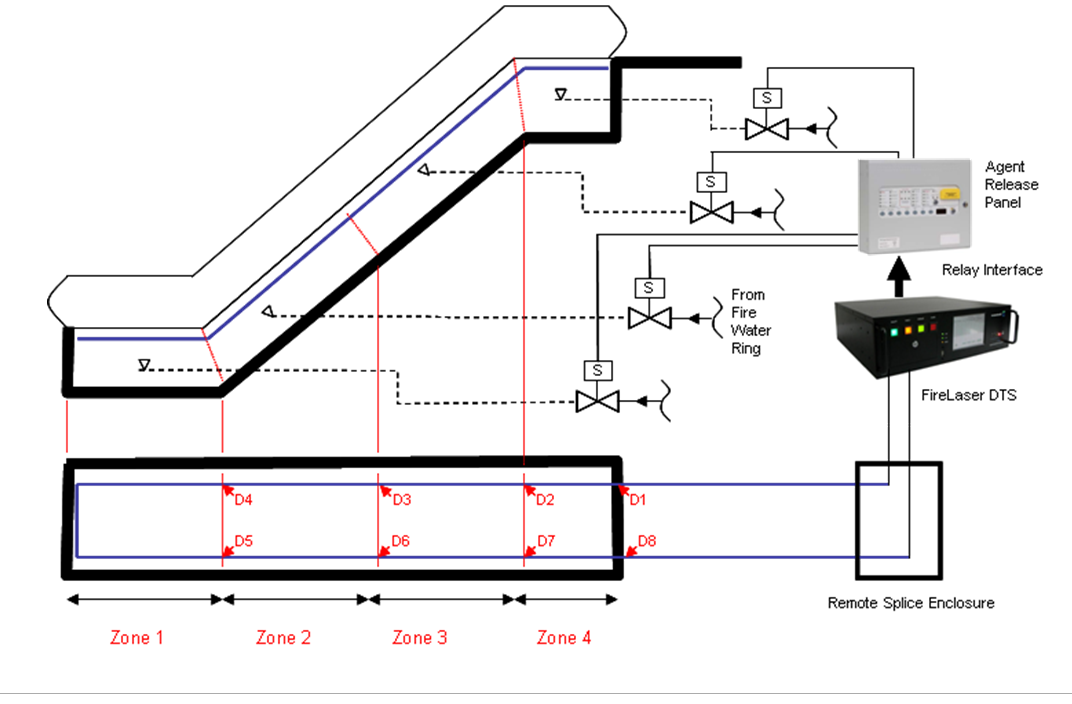
Escalator Protection
Escalators are vital for the convenient movement of people to and from large complex buildings. As such, escalators can form an integral part of a building’s emergency escape strategy. The decision as to whether an escalator should be used for the purpose of evacuation of personnel from a building in an emergency scenario is a complex one and there are many factors to consider when instigating a process of the possible adoption of escalators for emergency evacuation. This process may account for fire and certain non-fire incidents, such as Imminent Catastrophic Events (ICE). It is vital that the escalators and associated emergency egress routes are available at all times for their safe usage.
In light of the above, the main fire risks associated with escalators are due to:
- Faulty electrical equipment used to control the escalator movement and direction
- Roller bearings failure over time, which may lead to local overheating
- Associated hot works which may routinely be carried out in close proximity to the escalator
- Build-up of flammable materials discarded by personnel
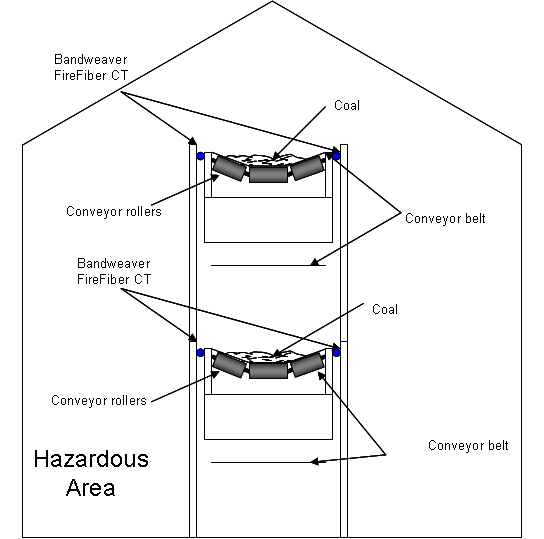
Conveyor Belt Protection
Generally there are two main characteristic fires that need to be detected at the earliest opportunity on belt type conveyors, a) moving and b) static fires. Moving fires are most commonly detected by infrared type technology, coupled sometimes with CO2 detection, located at strategic fixed point locations along the conveyor system. This strategy alone does not provide detection coverage over the entire belt length, and so it is common to introduce a linear heat detection solution to provide detection of the static fires and also the relatively large moving fires that can occur. Static fires can occur in close proximity to the belt and also to the electrical drive equipment associated with providing energy to the belt conveyor system.
The main fire risks associated with belt type conveyors are as follows:
- Friction due to loose of belt traction and slipping on the drive roller
- Welding activities can generate hot molten material
- Overheated materials placed on the belt
- Build-up of materials that have fallen off the belt and dust cloud generation
- Static electricity